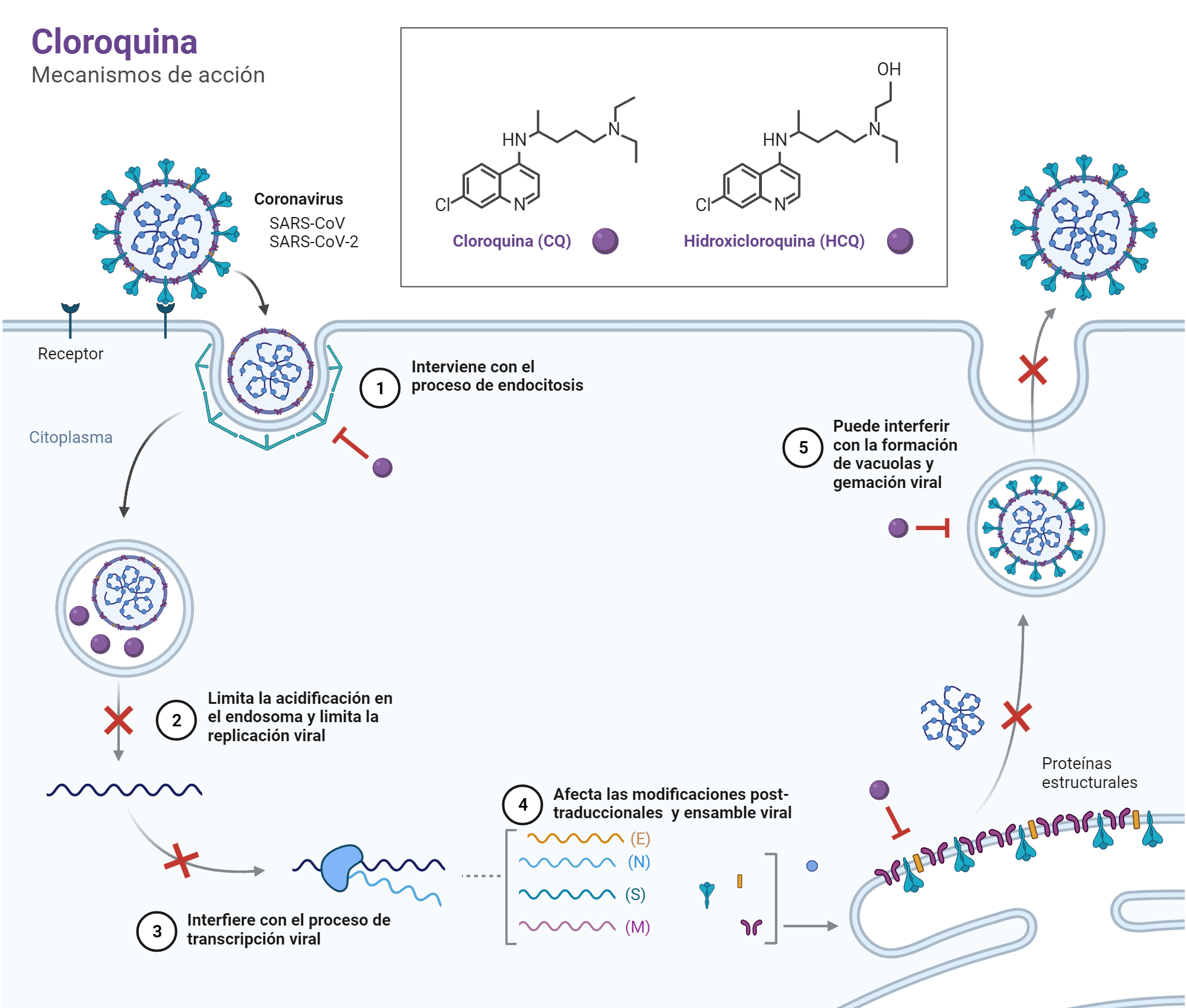
Cloroquina, a well-known antimalarial medication, has gained significant attention in recent years due to its potential applications beyond malaria treatment. Originally developed to combat malaria, this drug has been explored for its efficacy in treating a variety of other conditions, including autoimmune diseases and viral infections. Its versatility and the ongoing research make cloroquina a topic of great interest in the medical community and beyond.
The journey of cloroquina from its development to its current applications is both fascinating and complex. With a history that dates back to the 1930s, cloroquina has evolved in its usage and significance. Initially celebrated for its effectiveness against malaria, it has since been investigated for its potential role in managing diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis and lupus. Furthermore, recent studies have examined its potential in combating viral infections, including COVID-19, though with mixed results.
Understanding cloroquina's mechanisms, benefits, and limitations is crucial for both healthcare professionals and the general public. This article aims to provide a comprehensive overview of cloroquina, delving into its history, uses, potential side effects, and future prospects. By doing so, we hope to equip readers with the knowledge needed to better understand this multifaceted drug and its impact on health and medicine.
Read also:Wesley Snipes The Life And Legacy Of A Hollywood Icon
Table of Contents
- History of Cloroquina
- How Does Cloroquina Work?
- Uses of Cloroquina
- Cloroquina in Malaria Treatment
- Cloroquina and Autoimmune Diseases
- Is Cloroquina Effective Against COVID-19?
- Potential Side Effects of Cloroquina
- Who Should Avoid Cloroquina?
- Cloroquina Dosage Guidelines
- Cloroquina vs. Hydroxychloroquine
- Current Research and Developments
- What Are the Future Prospects for Cloroquina?
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Conclusion
History of Cloroquina
The history of cloroquina dates back to the 1930s when it was first developed as a treatment for malaria. Originally synthesized as a derivative of quinine, cloroquina was introduced as a more effective and less toxic alternative. Its development was a result of extensive research and collaboration among scientists seeking to combat malaria, a disease that had devastating effects on populations worldwide.
During World War II, cloroquina gained prominence as an essential medication for soldiers stationed in malaria-endemic regions. Its efficacy in preventing and treating malaria made it invaluable, leading to widespread use and recognition. Over the decades, cloroquina became a staple in the fight against malaria, saving countless lives and reducing the disease's burden.
However, the emergence of drug-resistant strains of malaria in the latter half of the 20th century posed new challenges. Despite resistance issues, cloroquina remained a key player in malaria treatment, especially in regions where resistance was less prevalent. Its history is a testament to its importance in global health efforts and its ongoing relevance in medical research.
How Does Cloroquina Work?
Cloroquina operates by interfering with the growth and reproduction of the malaria parasite within red blood cells. It achieves this by inhibiting the parasite's ability to degrade hemoglobin, a crucial process for its survival. By disrupting this process, cloroquina effectively halts the parasite's lifecycle, leading to its elimination from the host's body.
In addition to its antimalarial properties, cloroquina exhibits anti-inflammatory effects, which have been harnessed in the treatment of autoimmune diseases. This secondary mechanism involves the modulation of the immune response, reducing inflammation and alleviating symptoms in conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis and lupus.
Recent studies have also explored cloroquina's antiviral potential, examining its ability to inhibit viral replication. While some initial findings were promising, further research is needed to fully understand its efficacy and safety in treating viral infections like COVID-19. Nonetheless, cloroquina's multifaceted mechanisms continue to intrigue researchers and clinicians alike.
Read also:The Talent Behind Draco Who Plays Malfoy In Harry Potter
Uses of Cloroquina
Cloroquina's primary use is in the prevention and treatment of malaria. For decades, it has been a cornerstone in antimalarial therapy, particularly in regions where resistance is minimal. Its effectiveness in reducing malaria incidence and mortality has made it a vital tool in global health initiatives.
Beyond malaria, cloroquina is employed in managing autoimmune diseases, thanks to its anti-inflammatory properties. Conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis and lupus benefit from cloroquina's ability to modulate the immune system and reduce inflammation, improving patients' quality of life.
Moreover, cloroquina has been investigated for its potential antiviral effects, particularly during the COVID-19 pandemic. While its use in this context remains controversial, ongoing research aims to clarify its role and potential benefits. Overall, cloroquina's diverse applications highlight its versatility and importance in medicine.
Cloroquina in Malaria Treatment
Malaria, caused by Plasmodium parasites, remains a significant global health challenge, particularly in tropical and subtropical regions. Cloroquina has played a pivotal role in combating this disease, serving as both a prophylactic and therapeutic agent. Its effectiveness in reducing malaria transmission and mortality has been well-documented, making it a cornerstone of malaria control programs.
Cloroquina is typically administered as an oral medication, providing both preventive and curative benefits. In areas with low resistance, it remains highly effective, offering protection to travelers and residents alike. Its affordability and ease of administration further contribute to its widespread use in malaria-endemic regions.
However, the emergence of cloroquina-resistant strains of Plasmodium has necessitated the development of alternative treatments and combination therapies. Despite these challenges, cloroquina continues to be a valuable option in areas where resistance is low, underscoring its importance in the global fight against malaria.
Cloroquina and Autoimmune Diseases
Autoimmune diseases, characterized by the immune system attacking the body's own tissues, can cause significant morbidity and impact patients' quality of life. Cloroquina, with its anti-inflammatory properties, has been used to manage several autoimmune conditions, including rheumatoid arthritis and systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE).
In rheumatoid arthritis, cloroquina helps alleviate symptoms by reducing inflammation and slowing disease progression. Similarly, in lupus, it modulates the immune response, decreasing the frequency and severity of flare-ups. These effects make cloroquina a valuable addition to the therapeutic arsenal for managing autoimmune diseases.
Moreover, cloroquina's long history of use and established safety profile make it an attractive option for patients and clinicians. Its ability to provide symptom relief and improve quality of life underscores its significance in the treatment of autoimmune diseases.
Is Cloroquina Effective Against COVID-19?
The COVID-19 pandemic prompted a global search for effective treatments, with cloroquina emerging as a potential candidate. Early laboratory studies suggested that cloroquina could inhibit the replication of the SARS-CoV-2 virus, sparking interest in its use for COVID-19 patients.
However, clinical trials and observational studies have yielded mixed results. While some initial reports indicated potential benefits, subsequent research has questioned its efficacy and safety in treating COVID-19. Concerns about potential side effects, including cardiac issues, have further complicated its use in this context.
As of now, the role of cloroquina in COVID-19 treatment remains controversial. Ongoing research aims to provide more definitive answers, but current guidelines generally advise against its routine use for COVID-19 outside of clinical trials. Despite this, the exploration of cloroquina's antiviral properties has contributed to a better understanding of potential therapeutic options for viral infections.
Potential Side Effects of Cloroquina
While cloroquina is generally well-tolerated, it can cause side effects, some of which may be serious. Common side effects include gastrointestinal disturbances, such as nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea. These symptoms are usually mild and resolve with continued use.
More severe side effects, though rare, can occur. These include retinal toxicity, which can lead to vision problems, and cardiotoxicity, which may cause heart issues. Regular monitoring and adherence to recommended dosages can help mitigate these risks.
Patients with preexisting conditions, such as liver or kidney disease, may be at increased risk of side effects. As with any medication, it is essential to discuss potential risks and benefits with a healthcare provider to ensure safe and effective use.
Who Should Avoid Cloroquina?
Certain individuals should exercise caution or avoid using cloroquina altogether. Patients with known hypersensitivity to cloroquina or its components should not take the medication. Additionally, individuals with a history of retinal or vision problems should avoid cloroquina due to the risk of retinal toxicity.
Pregnant or breastfeeding women should consult with their healthcare provider before using cloroquina, as its safety during pregnancy and lactation is not fully established. Patients with cardiac conditions should also be cautious, given the potential for cardiotoxic effects.
Ultimately, the decision to use cloroquina should be made in consultation with a healthcare professional, considering individual health factors and potential risks.
Cloroquina Dosage Guidelines
Proper dosing of cloroquina is crucial to ensure its effectiveness and minimize the risk of side effects. Dosage varies depending on the condition being treated, patient age, weight, and overall health.
- For malaria prevention, cloroquina is typically taken once weekly, starting one to two weeks before travel to a malaria-endemic area and continuing for four weeks after leaving the area.
- In the treatment of malaria, a specific loading dose is followed by smaller doses over a few days.
- For autoimmune diseases, cloroquina is usually taken daily at a lower dose than for malaria treatment.
It is important to follow healthcare provider instructions and not to adjust the dose without consultation. Regular monitoring may be needed to ensure safety and efficacy, particularly for long-term use.
Cloroquina vs. Hydroxychloroquine
Cloroquina and hydroxychloroquine are closely related medications, both used in the treatment of malaria and autoimmune diseases. While they share similar mechanisms of action, there are key differences between the two.
Hydroxychloroquine, a derivative of cloroquina, is often preferred for autoimmune diseases due to its better safety profile and reduced risk of side effects. It is considered less toxic to the retina and generally better tolerated, making it a popular choice for long-term therapy.
In terms of efficacy, both drugs are effective in their respective indications, though their use may vary based on individual patient needs and the presence of drug-resistant malaria strains. Ultimately, the choice between cloroquina and hydroxychloroquine should be guided by a healthcare provider, considering factors such as safety, efficacy, and patient preference.
Current Research and Developments
Ongoing research into cloroquina continues to explore its potential applications and mechanisms. Studies are investigating its role in treating other infectious diseases and its impact on immune modulation. The exploration of cloroquina's antiviral properties remains an area of active investigation, with researchers seeking to understand its potential in combating various viral infections.
Additionally, advancements in drug formulation and delivery methods aim to enhance cloroquina's efficacy and reduce side effects. Innovative approaches, such as combination therapies, are being examined to overcome resistance and improve treatment outcomes.
As research progresses, cloroquina's potential applications and limitations will become clearer, contributing to a better understanding of its role in modern medicine.
What Are the Future Prospects for Cloroquina?
The future of cloroquina is shaped by ongoing research and the evolving landscape of disease treatment. As scientists continue to investigate its mechanisms and potential applications, cloroquina may find new roles in medicine.
Efforts to address drug resistance and improve safety profiles will be crucial in ensuring cloroquina's continued relevance. Additionally, its potential in treating emerging infectious diseases and autoimmune conditions remains a focus of research.
While challenges exist, cloroquina's long history of use and versatility suggest that it will continue to be an important tool in healthcare. Ongoing innovation and research will determine its future applications and impact on global health.
Frequently Asked Questions
- What is cloroquina primarily used for?
Cloroquina is primarily used for the prevention and treatment of malaria, as well as for managing autoimmune diseases like rheumatoid arthritis and lupus.
- Is cloroquina safe for long-term use?
Cloroquina can be safe for long-term use when prescribed by a healthcare provider and monitored appropriately. Regular check-ups are important to minimize the risk of side effects.
- Can cloroquina cure COVID-19?
There is no conclusive evidence that cloroquina can cure COVID-19. Its use for COVID-19 is generally not recommended outside of clinical trials.
- Are there any alternatives to cloroquina for malaria prevention?
Yes, there are several alternatives to cloroquina for malaria prevention, including medications like atovaquone-proguanil and doxycycline, depending on the region and resistance patterns.
- What should I do if I experience side effects from cloroquina?
If you experience side effects from cloroquina, contact your healthcare provider for advice. They may adjust your dosage or recommend alternative treatments.
- Is hydroxychloroquine the same as cloroquina?
Hydroxychloroquine is similar to cloroquina but has a better safety profile, making it a preferred choice for long-term treatment of autoimmune diseases.
Conclusion
Cloroquina is a versatile medication with a rich history and diverse applications in the treatment of malaria and autoimmune diseases. Its potential in treating viral infections, including COVID-19, has sparked significant interest, though its efficacy remains under investigation. While it offers numerous benefits, cloroquina is not without risks, and its use should be guided by healthcare professionals.
Ongoing research and innovation continue to shape cloroquina's role in modern medicine, with efforts to improve its safety and efficacy. As we look to the future, cloroquina's adaptability and versatility will likely ensure its continued importance in healthcare, contributing to improved outcomes for patients worldwide.
For more information, visit the World Health Organization (WHO) website for the latest guidelines and research on cloroquina and other treatments.
Article Recommendations